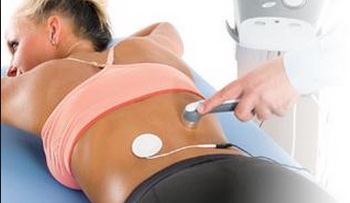
Ultrasonic waves or sound waves of a high frequency that is not audible to the human ear are produced by means of mechanical vibration in the metal treatment head of the ultrasound machine.
The treatment head is then moved over the surface of the skin in the region of the injury transmitting the energy into the tissues.
When sound waves come into contact with air it causes a dissipation of the waves, and so a special ultrasound gel is placed on the skin to ensure maximal contact between the treatment head and the surface of the skin and to provide a medium through with the sound waves can travel.
Ultrasound can also be applied under water which is also a medium for ultrasound waves to travel through.
Effects of therapeutic ultrasound
The effects of therapeutic ultrasound are still being disputed. To date, there is still very little evidence to explain how ultrasound causes a therapeutic effect in injured tissue. Nevertheless practitioners world wide continue to use this treatment modality relying on personal experience rather than scientific evidence. Below are a number of the theories by which ultrasound is proposed to cause a therapeutic effect.
Thermal effect
As the ultrasound waves pass from the treatment head into the skin they cause the vibration of the surrounding tissues, particularly those that contain collagen. This increased vibration leads to the production of heat within the tissue. In most cases this cannot be felt by the patient themselves.
This increase in temperature may cause an increase in the extensibility of structures such as ligaments, tendons, scar tissue and fibrous joint capsules.
In addition, heating may also help to reduce pain and muscle spasm and promote the healing process.
Effects on the inflammatory and repair processes
One of the greatest proposed benefits of ultrasound therapy is that it is thought to reduce the healing time of certain soft tissue injuries.
Ultrasound is thought to accelerate the normal resolution time of the inflammatory process by attracting more mast cells to the site of injury. This may cause an increase in blood flow which can be beneficial in the sub-acute phase of tissue injury. As blood flow may be increased it is not advised to use ultrasound immediately after injury.
Ultrasound may also stimulate the production of more collagen which is the main protein component in soft tissue such as tendons and ligaments. Hence ultrasound may accelerate the the proliferative phase of tissue healing. It is thought to improve the extensibility of mature collagen and so can have a positive effect to on fibrous scar tissue which may form after an injury.
